CURRENT ISSUE
March, 2026
No. 111 (3)
2024 Impact Factor: 7.9
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
EDITOR'S PICKS
Review Article
Diagnosis and management of adult telomere biology disorders
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Article
Ex vivo correction of severe coagulation Factor VII deficiency in patient-derived 3D liver organoids
Coagulation factor (F) VII deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease resulting from a wide spectrum of mutations in the F7 gene, and its clinical phenotype is extremely heterogenous. Roman and colleagues developed an autologous cell-based approach that corrects the disease-causing mutation in patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells and generates therapeutic, three-dimensional hepatic organoids. Their results represent a significant milestone toward the establishment of an autologous cell-based therapy for patients with FVII- and other coagulation factor deficiencies.
Letter
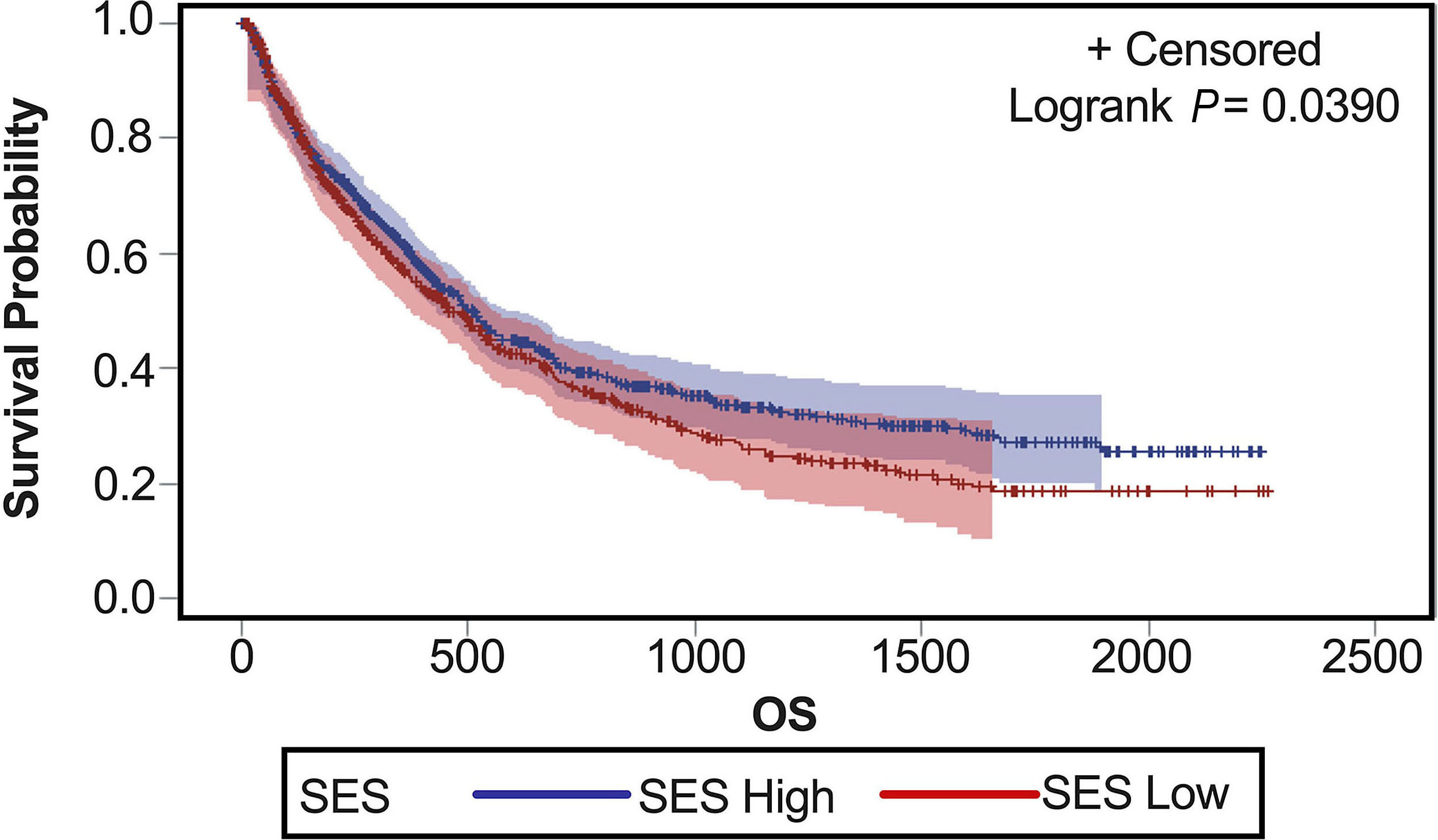
Impact of demographic factors on clinical outcomes of patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Prior studies suggest that non-white patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have inferior survival compared to white patients. Duarte and colleagues utilized the Flatiron Health database and analyzed AML outcomes by factors such as race, ethnicity, sex, and socioeconomic status (SES), with the goal of re-examining AML outcomes by demographic factors using a real-world dataset of academic and community centers. Results show that low SES, rather than ethnicity, impacts outcomes; in particular, low SES patients had worse overall survival, decreased utilization of novel agents, lower rates of clinical trial enrollment and transplant which impact survival.
Article
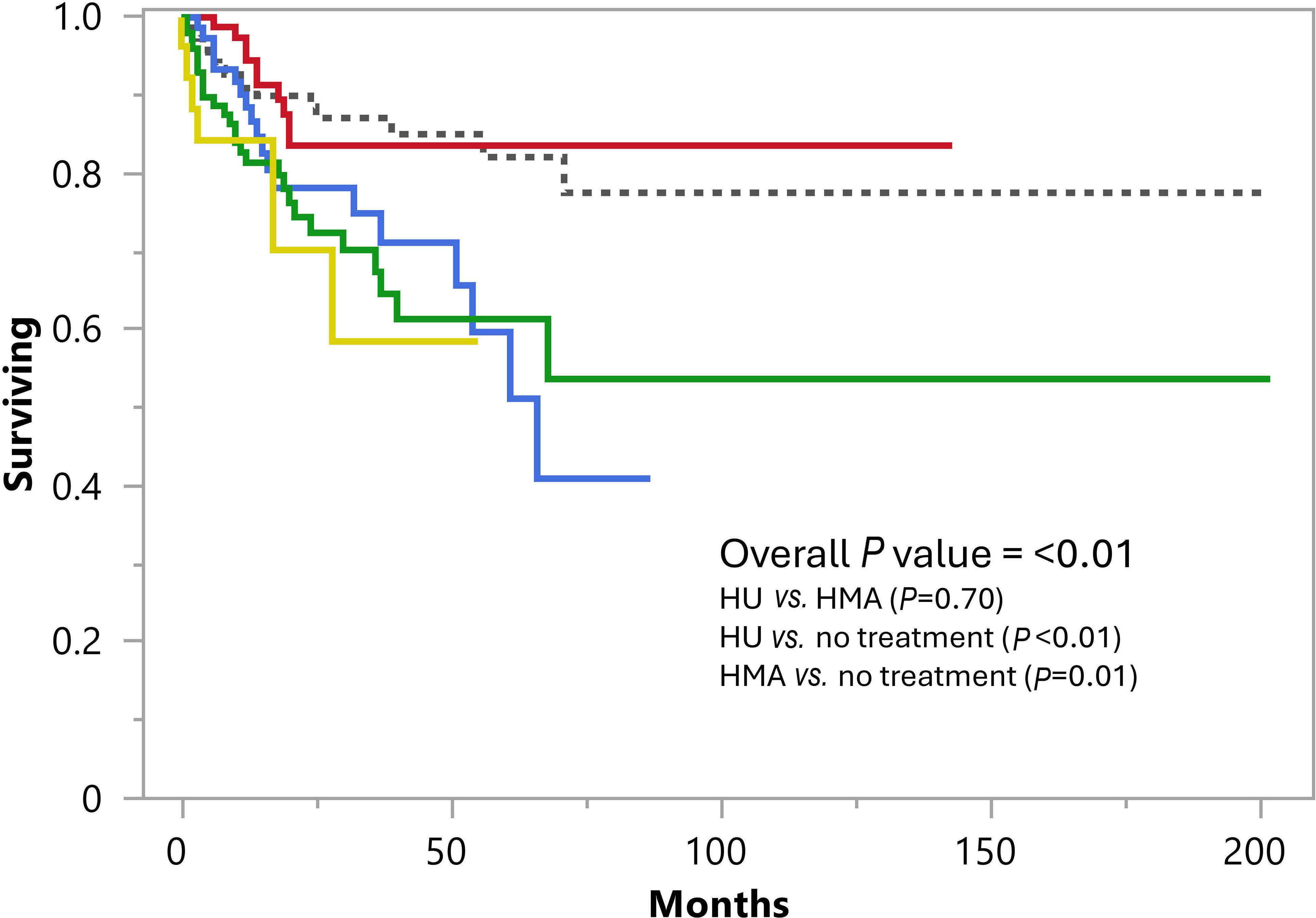
A retrospective analysis of upfront treatment strategies in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: impact on survival and response patterns
Current treatment strategies in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) do not control the genetic evolution of disease and blast transformation (BT) remains an inherent risk in these patients. The study of Yousuf and colleagues aimed to evaluate the impact of CMML-directed therapies on overall survival (OS), BT-free survival, and indication-specific responses. They confirmed that current drug therapy in CMML has no impact on OS but suggested a significant association between BT and the need for cytotoxic drug therapy.
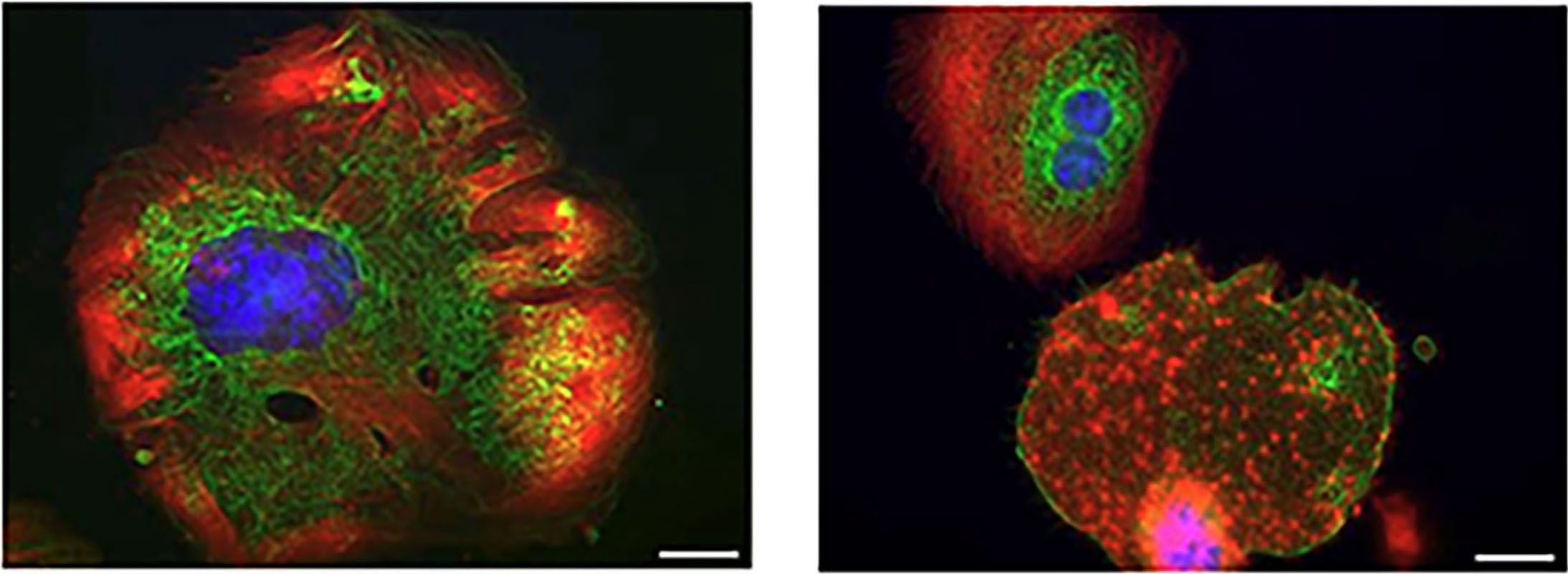
Letter
The co-inheritance of two ITGB3 variants with additive detrimental effects on platelets leads to variant Glanzmann thrombasthenia
Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GT) is an inherited platelet disorder typically caused by defects in the integrin αIIbβ3 receptor that impair platelet aggregation and lead to bleeding. Arndt and colleagues characterized a case in which two heterozygous ITGB3 gene variants were co-inherited and assessed their combined effects on platelet receptor expression and function using cellular models and patients’ cells. They found that the combined variants produce additive detrimental effects on αIIbβ3 expression and signaling, resulting in a variant form of GT with severe functional impairments of platelets.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA